WHAT IS BIODIVERSITY?
Biodiversity is the variety of life on Earth. Biodiversity is important because it supports essential services like food, clean water, and medicine, and helps ecosystems stay resilient and healthy, directly benefiting our wellbeing.
Farm to Ned Alliance: Biodiversity 101
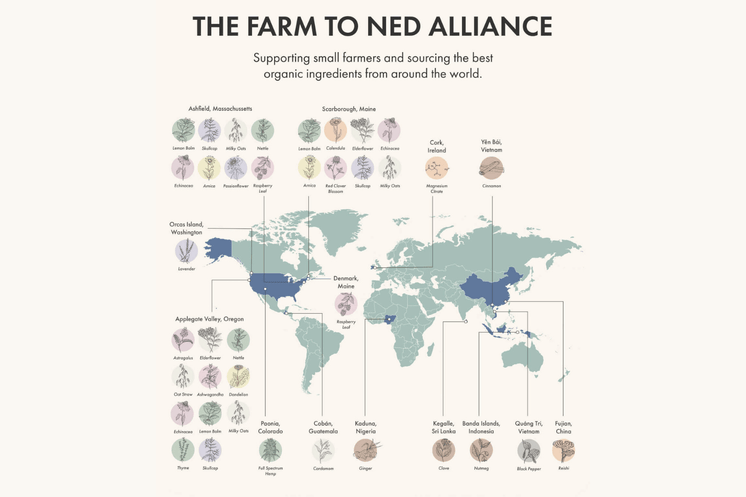
Biodiversity stands for biological diversity, and simply refers to the variety of all living things on our Earth. It is the foundation of life in our environment, microbiome, agriculture, and soil. Our current industrial food system is focused on productivity, pushing out as many crops and animals as fast as possible to stock our supermarkets. To be able to do this, factory farming, the use of pesticides, herbicides, and other chemicals have become the new norm. This has put the health of our plants, animals, and humans at risk (1). When our soil has biodiversity, our plants have a high concentration of vitamins and minerals, crops are naturally pest-resistant, they hold more water, and pesticides are not needed (2)! This is the foundation of regenerative farming, which restores the state of our soil and protects the future of our food systems. We are so grateful to partner with many amazing regenerative farmers through the Farm to Ned Alliance. Keep scrolling to see scientifically proven reasons why biodiversity is so important:
De-Stress Blend
De-Stress Blend is a natural path to stilling your waters and getting back to easier times. This blend is dominant in CBG – often referred to as the mother of all cannabinoids - and CBD, both extracted from the world’s purest full spectrum hemp and features a botanical infusion of ashwagandha, cardamom and cinnamon.
60-day Stress Free Guarantee
Simply place your order. Your 60-day trial begins from the day your order is delivered.
Start using your Ned product. Our Customer Happiness Team is here to give you all the guidance you need.
If you want to break things off, no hard feelings. Contact our Customer Happiness Team and they’ll help you out. Simple.
**Valid for one product at a time - bundles not eligible
mellö Magnesium - 30 Travel Sticks
30 Single Serve Packets
60-day Stress Free Guarantee
Simply place your order. Your 60-day trial begins from the day your order is delivered.
Start using your Ned product. Our Customer Happiness Team is here to give you all the guidance you need.
If you want to break things off, no hard feelings. Contact our Customer Happiness Team and they’ll help you out. Simple.
**Valid for one product at a time - bundles not eligible
1. Foundational for Human Health
The human microbiome is our internal farm that needs to be nourished. These healthy bacteria affect every aspect of our life: from gut health, the immune system, cardiovascular system, and even our thoughts! Did you know the soil also has a thriving microbiome, which is very similar to our own (3)? When chemicals are sprayed in the soil, we slowly start to kill the bacteria off. When we eat the food from this soil, our bodies will mimic the same pattern. This is part of the reason why it is so difficult to get enough vitamins and minerals in our diet. When our ecosystems are healthy, they will naturally purify our water, nourish our bodies with smaller portions of food, and supplementation would not be as necessary.
2. Prevention of Infectious Diseases
In the aftermath of a pandemic, most of us are aware of how important it is to prevent the spread of diseases. When we cut down forests to create factory farms, we are tearing down the homes of natural wildlife, who then are forced to move closer to humans. Studies have shown 75% of all new diseases come from wildlife. When there is a lack of biodiversity in animals and soil, instead of the diseases being kept within specific animal species, they easily spread to humans and can mutate within our bodies (4).
3. Connection to the Climate
By cutting down our forests to create factory farms, we have accelerated the speed of climate change. Forests are essential for water and air filtration and cooling the global temperatures. Our forests are the natural way our Earth removes CO2 from the environment, which is why we need to preserve the ones we have left (5).
4. Relationship to Western and Eastern Medicine
Medicine is created and extracted from life such as fungi, animals, and plants. Traditional Chinese Medicine and Herbalists work with herbs, mushrooms, and seaweeds to create natural medicine, but did you know even our Western Pharmaceuticals are dependent on biodiversity? Many lifesaving antibiotics and other medicines are created from natural sources, and upwards of 70,000 plants are used for their medicinal properties (6).
References
- FoodPrint. (2021). Biodiversity and agriculture. URL: https://foodprint.org/issues/biodiversity-and-agriculture/
- Shroff, R., & Cortés, C. R. (2020). The Biodiversity Paradigm: Building Resilience for Human and Environmental Health. Development (Society for International Development), 63(2-4), 172–180. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41301-020-00260-2
- Hirt, H. (2020). Healthy soils for healthy plants for healthy humans: How beneficial microbes in the soil, food and gut are interconnected and how agriculture can contribute to human health. EMBO reports, 21(8), e51069. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.202051069
- Kulkarini, S. (2022). Biodiversity loss can increase the spread of zoonotic diseases. Biodiversity Loss Can Increase the Spread of Zoonotic Diseases. https://sitn.hms.harvard.edu/flash/2022/biodiversity-loss-can-increase-the-spread-of-zoonotic-diseases/
- Forests fight for the climate. (2024). Rainforest Action Network. https://www.ran.org/issue/forests-fight-for-the-climate/
- Marshall A. C. (2020). Traditional Chinese Medicine and Clinical Pharmacology. Drug Discovery and Evaluation: Methods in Clinical Pharmacology, 455–482. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-68864-0_60
- Taylor, L. H., Latham, S. M., & Woolhouse, M. E. (2001). Risk factors for human disease emergence. Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological sciences, 356(1411), 983–989. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2001.0888